Offering credit sales to customers is a common practice among many enterprises. Now that you’ve got a clearer understanding of the practical applications for net realizable value, let’s take a closer look at what these figures can tell you about your business. After all, you can then use this information to action necessary changes that will take your company to the next level. Kenneth W. Boyd has 30 years of experience in accounting and financial services. He is a four-time Dummies book author, a blogger, and a video host on accounting and finance topics.
AccountingTools
Understanding NRV will help you make more informed financial decisions and improve your business’s financial health. US GAAP does not permit a write-up of write-downs reported in a prior year, unlike international reporting standards, even if the net realizable value for inventory has been recovered. It is worth noting that the adjustments can be made for each item in inventory or for the aggregate of the entire net realizable value inventory to the lower cost or NRV. Once curtailed down, the inventory account becomes the new basis for reporting purposes and valuation. Depending on the industry the company is it, the company may decide to accept a certain amount of uncollectable sales. Although we endeavor to provide accurate and timely information, there can be no guarantee that such information is accurate as of the date it is received or that it will continue to be accurate in the future.
NRV: What Net Realizable Value Is and a Formula To Calculate It
If appropriate decisions are to result based on this information, both the preparer and the reader need an in-depth knowledge of U.S. The firm remains concerned about evaluating the assets properly, which makes calculating NRV a conservative approach, indicating that the firm should not overstate the profit by showing a lesser value of its assets. The calculation for Net Realizable Value has a variety of methods to get an answer. No matter which method you use to find the NRV, the value you find must fit the conservative method of accounting reporting.
IAS 2 generally measures inventories at the lower of cost and NRV; US GAAP does not
Cost includes not only the purchase cost but also the conversion and other costs to bring the inventory to its present location and condition. If items of inventory are not interchangeable or comprise goods or services for specific projects, then cost is determined on an individual item basis. Conversely, accumulated depreciation definition when there are many interchangeable items, cost formulas – first-in, first-out (FIFO) or weighted-average cost – may be used. Techniques for measuring the cost of inventories, such as the standard cost method or the retail method, may be used for convenience if the results approximate cost.
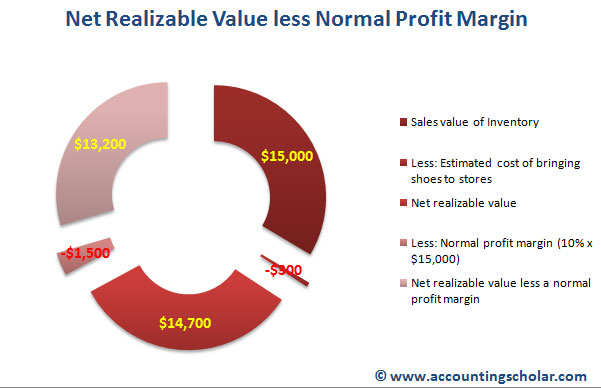
- The conservative principles involved in the calculation prevent the overstatement of assets.
- Additionally, considering customer liquidity problems or poor economic conditions, the company prudently anticipates that $300 may not be recoverable due to potential bad debt, aligning with the principle of conservatism.
- NRV provides a conservative estimate of an asset’s value, ensuring financial statements reflect realistic asset valuations.
The general concept is to factor in the worst-case scenario of a firm’s financial future. Uncertain liabilities are to be recognized as soon as they are discovered. In contrast, revenues can only be recorded when they are assured of being received.
Volkswagen disclosed ownership of €43.7 billion of inventory, a very slight decline from the €43.8 billion of inventory carried at the end of December 2020. Because it is used in several different situations, net realizable values can tell analysts and accountants several important pieces of information. Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University.
It’s a more streamlined approach, which aligns with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and is considered to represent a more focused reflection of the net amounts expected to be realized from inventory sales. Sometimes, external valuation services or appraisals might be required, especially when dealing with specialized or infrequently traded assets. Gathering as much information as possible about what similar assets are selling for will be crucial to forming a reliable basis for the expected selling price.
In general, US GAAP does not permit recognizing provisions for onerous contracts unless required by the specific recognition and measurement requirements of the relevant standard. However, if a company commits to purchase inventory in the ordinary course of business at a specified price and in a specified time period, any loss is recognized, just like IFRS Standards. If a company has a contract to sell inventory for less than the direct cost to purchase or produce it, it has an onerous contract.
Net realizable value for inventory is the estimated selling price of inventory in the ordinary course of business, minus the estimated costs of completion and sale. For instance, if inventory sells for $500 and costs $100 to complete and sell, the NRV is $400, reflecting the inventory’s true market value. Inventory represents a significant part of the balance sheet for many companies. In accounting for inventory determining and capturing the costs to be recognized as an asset through the inventory lifecycle is key, because it affects a company’s KPIs such as gross profit margin. Despite similar objectives, IAS 21 differs from ASC 330 in a number of areas2. Here we summarize what we see as the main differences on inventory accounting between the two standards.
The first step of the process is determining your asset’s fair market value (FMV). And in a market with heavy competition, to maintain your sales levels, you have to keep your price competitive (for the Sassy purses, say $50 per unit or lower). If your total costs come in lower than expected, maybe you can price the product lower than $50, and that might increase sales. IBM is a US-based software company with more than $80 Bn of revenue per year. In the Financial year 2019, the market value of Accounts Receivable (which is an asset) for IBM is $10 Bn.